The Use of Submicron Lipid Matrix-Encapsulated Actives Offers a Multitude of Advantages for the Overall Performance of Skin Care Formulations
Sabilla Digel – Berg+Schmidt
Formulating with actives can be a challenge
Lately, skin care consumers have been developing increasing expectations when it comes to their skin care, especially facial care. In the post-pandemic world, the so-called skinification of beauty is on the rise. It means that beauty is not achieved by putting on makeup, but by actually improving the health of our largest and most visible organ, the skin. Improving the state of the skin at the cellular/molecular level – whether that means reducing wrinkles, fighting oxidative stress and skin aging, or promoting healthy cell turnover – is achieved by active ingredients that really do their job. Scientifically-based evidence for the efficacy of cosmetic formulations and actives has gained substantial importance. But in order for an active to reach its target in the skin, it must penetrate the upper skin layers in a sufficient concentration, which is sometimes limited due to solubility issues, stability issues, incompatibility with the formulation or poor penetration of the active into the skin. To improve efficacy, the concentration of the active should not be simply increased at will, as this involves a certain risk since there is often a lack of data on tolerability at higher concentrations . Therefore, it is better to increase the efficacy at a typical concentration through technologies that enhance performance.
Submicron lipid particles as delivery systems
Submicron lipid particles are very small “droplets” from 0.1-1.0 µm in size which are solid at room and skin temperature, typically with a melting range above 40 °C. They consist of one solid (SLN = solid lipid nanoparticles), one solid and one liquid (NLC = nanostructured lipid carriers) or multiple solid and liquid lipids (BCSL = BergaCare SmartLipids). Lipophilic actives, even those with poor lipid solubility, can be embedded within these particles which can then be stabilized as an aqueous suspension. The latest generation and most complex system, BergaCare SmartLipids, shows less polymorphic transitions by reordering of the lipid crystal structures, and therefore enhanced ability to hold the active over the shelf life of the product. This is achieved by a careful design of the lipid matrix surrounding the respective active, meaning that each lipid matrix and each production process is specific to the active to be encapsulated.
If a product with SmartLipids, e.g. an aqueous serum, is applied and distributed on the skin (Figure 1), the water slowly evaporates, leaving a uniform, very thin SmartLipids layer on the stratum corneum. SmartLipids adhere well to the skin due to their lipidic character and their submicron size which results in a higher possible surface in interaction with the skin. During rubbing, the SmartLipids partly fuse, forming a semi-occlusive patch that – together with the warm skin temperature – promotes the release and penetration of the embedded active into the stratum corneum and beyond, unfolding its beneficial effects in the skin.

Fig. 1. Submicron lipid particles / SmartLipids applied to skin
Benefits of submicron lipid particle-based delivery systems
In summary, the following benefits can be achieved when actives are encapsulated via carefully designed submicron lipid particles.
- Increased efficacy compared to the free active
- Restoration of impaired skin barrier
- Increased consumer acceptance through improved sensory and rheological properties
- Formation of a semi-occlusive protective barrier, resulting in reduced TEWL and increased skin hydration
- Increased active penetration through “invisible patch effect”
- Easy to formulate with (instantly water-dispersible)
- Improved handling of problematic actives (poor solubility or chemical lability)
- Cold processing, no risk of breakage at common shear rates
- Good adherence to the skin, prolonged and controlled release
- Reduction of adverse effects from the active
- Stabilization of labile ingredients
- Completely natural design of the SmartLipids possible
- Further advantages specific to the active
- Tailor-made solutions
The aspects highlighted in blue are topics treated in below in this article.
The following actives have been encapsulated by SmartLipids technology and are commercially available (further developments are continuously ongoing):
- Coenzyme Q10
- Retinol
- Glabridin
- Ceramides
- Bakuchiol
- Custom solutions (exclusive developments)
Increased efficacy compared to the free active
Bakuchiol, a monomolecular extract of Psoralea coryfolia (babchi plant), is a very popular cosmetic active with a multitude of effects, including anti-wrinkle, anti-hyperpigmentation, anti-inflammatory, and radiance-increasing effects. Due to its good tolerability at a concentration of 0.5%, it is often considered a natural and non-irritating alternative to retinol.[1-3] However, the study landscape, especially when it comes to placebo-controlled in vivo studies, is very limited. Now it has been demonstrated that BergaCare SmartLipids Bakuchiol exhibits the positive effects of free, non-encapsulated bakuchiol with even better performance. In a placebo-controlled study 3 different formulations were tested, a standard O/W lotion with 0.5% free bakuchiol, the same standard lotion with 0.5% bakuchiol encapsulated in the form of BergaCare SmartLipids Bakuchiol, and as a negative control the standard lotion without any active (placebo).[4]
Wrinkle depth was measured by Primos 3D (Fig. 2, left). The formulation with encapsulated bakuchiol reduced wrinkle depth faster and to a greater extent than the formulation with free bakuchiol (30% more reduction after 12 weeks of use). The crow’s feet area of an example volunteer is shown in Fig. 3, where a clear reduction of some wrinkles can be seen. The placebo did not have any effect on wrinkle reduction.
The firmness R0, as measured by cutometer, is the ability of the skin to withstand deformation due to an underpressure inside the measurement device probe. A reduced R0 value means higher skin firmness. Both formulations with free bakuchiol and encapsulated bakuchiol were able to improve skin firmness, while the formulation with the encapsulated bakuchiol showed a significant improvement already after 4 weeks. After 12 weeks of use it was 37% more effective than with free bakuchiol. It should be noted that even the placebo formulation without bakuchiol showed an improvement of R0 as well, but to a clearly lesser extent than formulations containing 0.5% active.
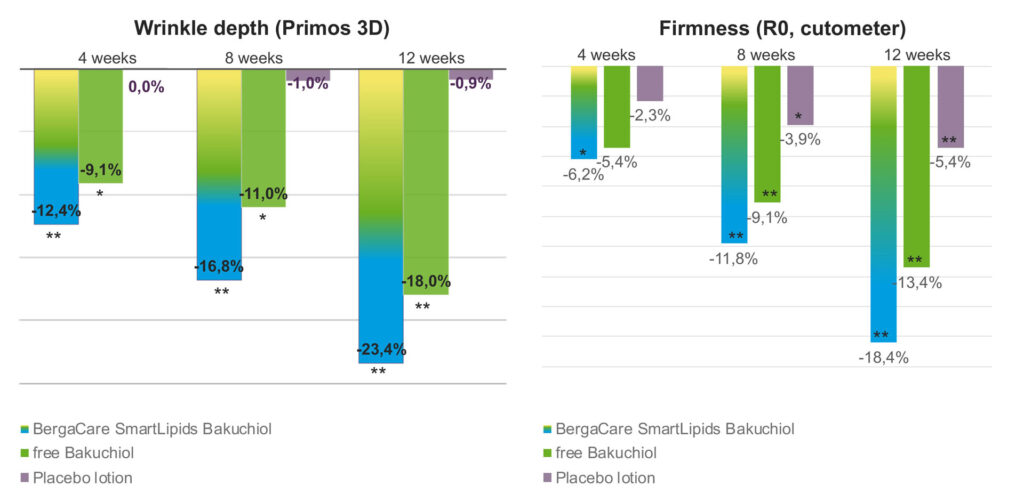
Fig. 2. Effects on wrinkle depth and skin firmness by BergaCare SmartLipids Bakuchiol. Study design: 30 volunteers (Caucasian, female, min. 40 years old with visible wrinkles in crow’s feet area) were recruited and each volunteer was assigned 2 formulations through a randomized split-face design, meaning that each of the 3 formulations was tested on 20 volunteers. Application 2x daily for 12 weeks. Measurements were done at least 8 h after the last product application on cleansed skin and with an acclimatization period. Significance vs baseline: * p<0.05 (95%),** p<0.01 (99%).

Fig. 3. Wrinkle reduction (crow’s feet area) of a representative volunteer no. 16 using a lotion with BergaCare SmartLipids Bakuchiol (total 0.5% bakuchiol). Left: before use. Right: after 12 weeks of 2x daily use.
Furthermore, no adverse reactions were reported for any volunteers from any of the 3 formulations, which makes BergaCare SmartLipids Bakuchiol (and bakuchiol in general) a very safe product to use in the tested concentration of 0.5%.
Restoration of the skin barrier
Submicron lipid particles in a topical formulation are able to improve or restore the moisturization and moisture retention of the skin a) by forming a very uniform protective film which reduces the TEWL, b) by the encapsulated actives where they influence skin moisture management, c) by directly providing building blocks to the skin – such as ceramides – which occur naturally in the stratum corneum.
Formation of a semi-occlusive, protective film
In a study (in vivo with 31 volunteers) with a commercial cream containing coenzyme Q10 encapsulated in submicron lipid particles, it was demonstrated that skin hydration was significantly higher than with the same cream with the free active Q10 after 4 and 6 weeks of daily usage.[5] This showed that the lipid matrix itself, having a small submicron size and being in a solid state at skin temperature, is active in improving skin moisture through physical protection of the skin surface. Even 7 days after stopping usage of the cream, the increased skin hydration of the submicron lipid particle cream was still measurable, while the hydration values for the control returned to the original state before the study.
Providing barrier building blocks to the skin
In the stratum corneum, the uppermost layer of the epidermis, dead skin cells are embedded in a lipid mixture in what is commonly known as a brick and mortar structure (bricks = skin cells; mortar = intercellular cement). The intercellular lipids consist mainly of ceramides, cholesterol and fatty acids. These three classes of molecules form lamellar structures between the cells that limit the passive diffusion of water to the outside world. In fact, without this essential part of the skin barrier, human life would be impossible. BergaCare SmartLipids Ceramide mimic the natural components of the intercellular lipids of the stratum corneum, as they contain ceramides, plant-based phytosterols (as alternatives to animal-based cholesterol), and fatty acids. This product was designed to emulate the typical composition of naturally occurring skin barrier lipids.
In an ex vivo study, the effect of BergaCare SmartLipids Ceramide on the TEWL of healthy skin explants was tested (Fig. 4). The product was applied in the form of an aqueous submicron lipid suspension at two different dilutions, 2.5% (=0.175 total ceramides) and 5% (= 0.35% total ceramides), and the evolution of the TEWL over time was measured by tewameter.
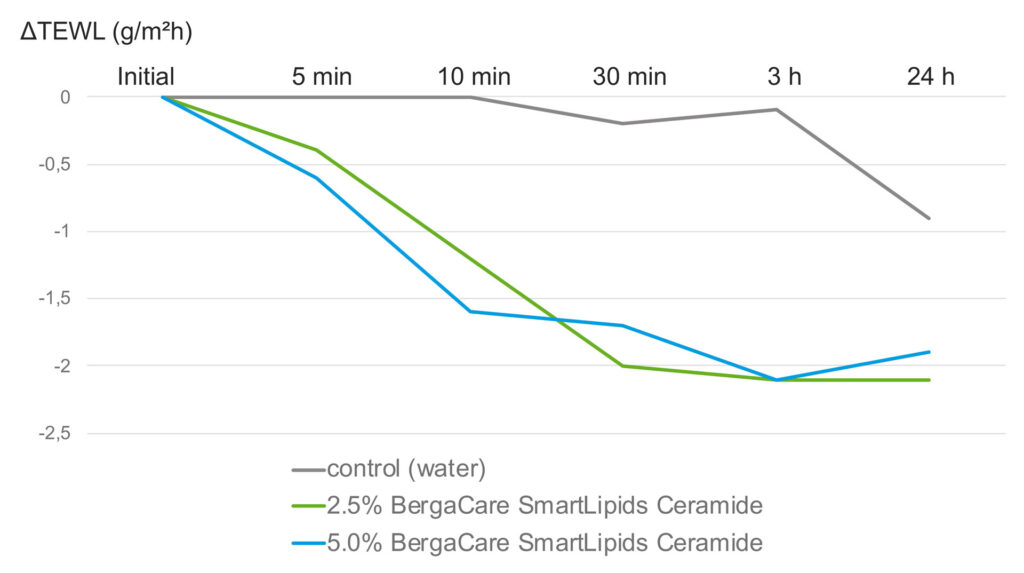
Fig. 4. Reduction of TEWL on healthy skin explant by application of encapsulated ceramides at two different concentrations
It can be noted that the TEWL was quickly reduced at both use concentrations – after just 5 minutes – and reached a good and stable low level at 30 min – 3 h. It can be concluded that the submicron lipid particles are very potent at reducing the TEWL instantly and over several hours. As the difference between the samples and the negative control reduced notably after 24 h, this is an indirect clue that the full TEWL-reducing effect does not persist after 24 h and a new product application might be necessary.
To further shed light on the question of whether the skin barrier restoration effect is reached by the formation of a physical barrier alone in form of a submicron lipid particle film on the skin, or if the ceramides actually penetrate into the stratum corneum, a further investigation was carried out. Here, healthy skin explants were delipidated according to a standard protocol (tape stripping, repeated washing and wiping with ethanol, acetone and ether) to simulate dry skin that exhibits a weak skin barrier. The delipidated skin explants were then treated with the two different dilutions of BergaCare SmartLipids Ceramide.
The presence and quantity of ceramides in the stratum corneum was then visualized by immunostaining of skin sections at different points in time with a purple dye and semi-quantification by image analysis (n = 9 for each explant). The results are obtained as a percent (%) value of the surface positive to purple immunostaining.
In normal skin, an average of 25% ceramide content is found in the stratum corneum. In delipidation a significant amount of the intercellular lipids (including ceramides) is removed. After 3 h only 15% ceramides were detected in delipidated skin, rising to 22% after 24 h, which shows that the skin clearly has the ability to almost completely recover its deficiency within a day.
When ceramides were applied in form of submicron lipid particles, we can see that ceramides began to penetrate the upper layers of the stratum corneum. With a ceramide content of 21% after 3 h, the levels were 44% better than without the product application, in other words, the stratum corneum recovered almost as well in 3 h as the skin was able to recover on its own after 24 h. Furthermore, a clear ceramide gradient can be seen: the concentration is higher at the upper stratum corneum layers, which means the new ceramides definitely originated from the surface in the form of a topical product, while the natural synthesis of ceramides in the skin takes place in the lower part of the stratum corneum. After 24 h hours, the ceramide level increased to 33% where the product had been applied, which is 50% more than without product treatment.
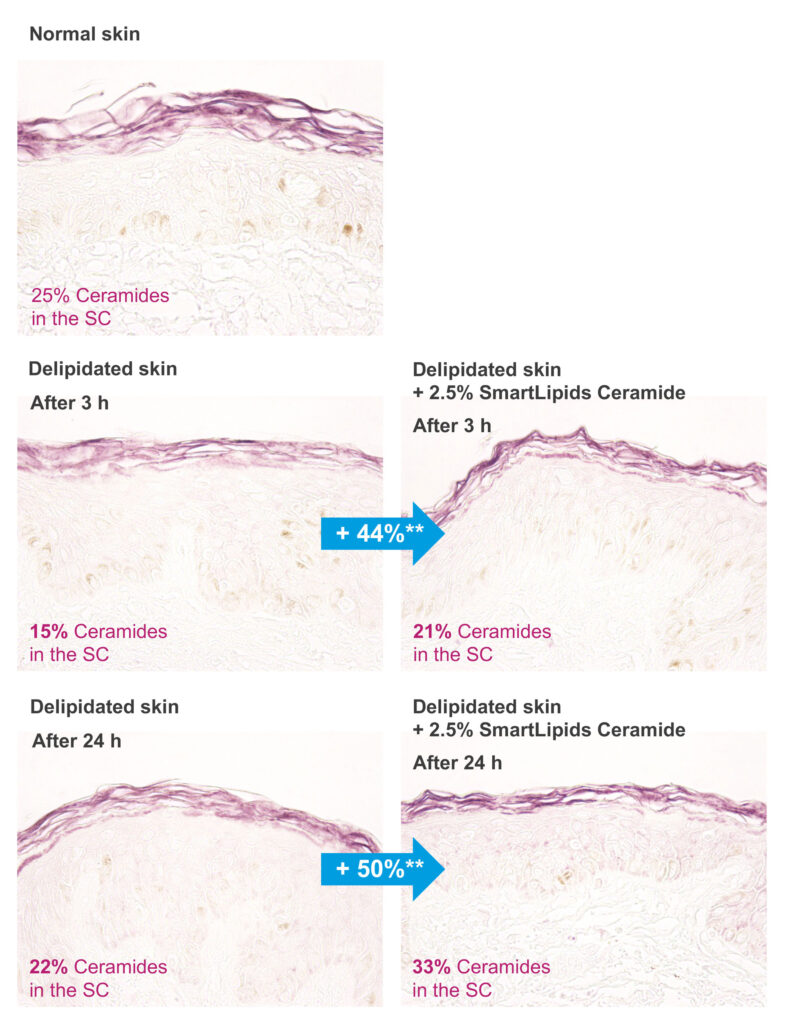
Fig. 5. Visualization of ceramide content in the stratum corneum (purple staining) in normal skin, delipidated skin after 3 and 24 h, and delipidated skin + 2.5% BergaCare SmartLipids Ceramide after 3 h and 24 h. Significance vs delipidated skin without product application: ** p<0.01 (99%)
In conclusion, it was demonstrated that submicron lipid particles not only improve the TEWL of intact skin, but can also be used to quickly restore an impaired skin barrier.
Increased consumer acceptance through improved sensory and rheological properties
When a skincare product is formulated with submicron lipid particles, its rheology and sensory properties are generally improved. Products typically exhibit a significantly higher apparent viscosity (Table 1), a more pronounced thixotropy and a higher yield point, which leads to a more pleasant sensory perception by the consumer that can positively influence product acceptance and estimated subjective efficacy.[5] Furthermore, oily ingredients can appear less sticky or oily on the skin when their sensory properties are “masked” by the surrounding solid lipid matrix.
| Standard lotion | |||
| Phase | Trade name / product | INCI | % |
| A | Demin. water | Aqua | Ad. 100% |
| Keltrol CG-SFT | Xanthan Gum | 0.30 | |
| Glycerin | Glycerin | 1.00 | |
| B | BergaCare SB | Butyrospermum Parkii (Shea) Butter | 5.00 |
| BergaCare FG Olive | Hydrogenated Ethylhexyl Olivate and Hydrogenated Olive Oil Unsaponifiables | 10.0 | |
| BergaBest GS SE | Glyceryl Stearate SE | 3.00 | |
| Vegarol 1618 | Cetearyl alcohol | 2.50 | |
| C | Citric acid (25% aq.) | Citric Acid | adjust pH to 5.1-5.3 |
| D | Euxyl PE 9010 | Phenoxyethanol (and) Ethylhexylglycerin | 1.00 |
| E | Fragrance | Parfum | 0.10 |
| 100,00 |
Internal Ref.: PF-022D-BSC
| Formulation | Viscosity after 1 h | Viscosity after 24 h |
| Standard lotion | 960 mPas | 1320 mPas |
| Standard lotion with 10% BergaCare SmartLipids Bakuchiol | 4900 mPas | 8100 mPas |
Table 1. Composition of a standard cream and Brookfield viscosities (20 rpm) with and without submicrometer lipid particles.
Conclusion
Submicron lipid particles are a high-tech approach to common challenges with cosmetic actives, with many practical benefits. Advantages arising from the technology itself (increased efficacy, controlled and prolonged release, restoration of the skin barrier, easy handling, protection of sensitive actives, worry-free and homogeneous incorporation of poorly soluble actives) can be combined with the individual benefits of specific actives.
[[1]] R. K. Chaudhuri, K. Bojanowski, Int. J. Cosmet. Sci., 2014, 1–10.
[2] S. Dhaliwal et al., Br. J. Dermatol. 2019, 180, 289–296.
[3] A. Bluemke et al., Int. J. Cosmetic Sci. 2022, 44, 377–393.
[4] Berg+Schmidt GmbH & Co KG, unpublished results as of 11/2022.
[5] J. Pardeike, K. Schwabe, R. H. Müller, Int. J. Pharmaceutics, 2010, 396, 166-173.
Share this article
Back to News